TECHNICAL TIPS FOR BETTER PERFORMANCE OF YOUR PNEUMATIC PUMP
Compartilhamos abaixo 10 dicas técnicas para obter o melhor desempenho de sua bomba de diafragma pneumática. Confira:
1) Mantenha sempre um kit de reparos na mão.
Não há uma lista de peças de reposição recomendadas, mas seria melhor manter sempre um kit de reparo lateral fluido e lateral de ar à mão para todas as bombas.
Esses kits geralmente são abastecidos com peças de desgaste, e podem corrigir a maioria dos pequenos avarias para manter suas bombas funcionando.
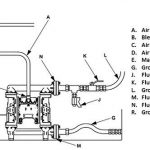
2) As bombas de diafragma operadas a ar são projetadas para ter assistência de gravidade.
Use essas dicas para experimentar o melhor desempenho.
a. Instale bombas com os “pés no chão”.
B. Keep the entry and exit vertical with each other.
w. The inlet must be at the bottom of the pump.
If you don't, they might not work.
3) The configuration number is the DNA of a pump.
This is how you find the material your diaphragm, ball, seat, hose, etc.
Locate the configuration number on the pump's metal tag. Then use the manual to decode the number.
This tells you what material the pump is made of, the internal components, motor and other accessories.
4) AVOID running the diaphragm pump dry.
Being dry, it increases the speed of the pump.
This adds wear and tear to your wetted parts (diaphragms, balls, seats).
5) Choose a pump based on your flow rate.
The pump flow rate listed in the literature is the MAX flow rate under perfect conditions.
You will want to select a pump that can achieve the desired flow rate at the desired pressure.
To determine this, consult the performance charts for each pump.
6) Does your pump have any of the problems below?
• Faulty pumping
• Reduced performance
• Low flow rates
• High discharge pressure
You may have a mismatched hose for your pump size.
For best performance, we recommend that your suction and discharge line sizes are equal to or larger in size than your pump.
7) There are 4 metals typically used in the diaphragm
a) aluminum
By far the most common. About 70% of all diaphragm pumps are aluminum. It's inexpensive, durable, lightweight, and works with a wide range of materials.
b) stainless steel
It has more abrasion and chemical resistance than aluminum, but is more expensive and heavier.
c) Cast or ductile iron
one. Often used in wastewater applications. Good abrasion resistance. Handles particles and solid materials well. More expensive than aluminum
d) Hastelloy
Not often seen in diaphragm pumps, it is quite cost prohibitive. It can be up to 6 times more expensive than stainless steel because of the high nickel content. Hastelloy is more PH and chemical resistant than stainless steel.
8) Plastic diaphragm pumps work very well in many applications. There are some applications where you will want to consider a metal pump before a plastic one.
a) Straight wastewater. Plastic pumps do not handle the abrasives in the wastewater sump.
b) Oil. Plastic pumps are chemically compatible with petroleum but are more expensive than aluminum which handles petroleum well. Save money and use aluminum with petroleum.
9) Plastic pumps can be used in almost any application, but they really are better:
-
Chemical Processing
· Highly concentrated chemicals
· Semiconductor Industry
· Transfer of solvents, such as in ink discharge lines, for example
· Strong cleaning detergentsWhenever you are dealing with a chemical that is high on the acid or base scale, you will need to use a plastic pump.
PROS:
Plastics are a very versatile and compatible material. Almost any application could use a plastic pump.
There is no metal in the fluid path. This means that plastic has great resistance to corrosion. Aggressive caustic chemicals are no problem.
Plastic pumps are much lighter than metallic pumps. If you need to move a pump around your facility consider going plastic.
CONTRAS:
Polypropylene is not a UV stable plastic. Left in the sun too long and you'll start to see scale. UV inhibitors add extra cost and reduce chemical compatibility. If using plastic pumps outdoors use PVDF, Kynar or conductive polypropylene.
If you pump in cold weather, be aware of the minimum operating temperatures for plastic pumps. When it gets really cold, you may experience fluid sections cracking. If you need temporary cold resistance look to metal pumps.
What other pros and cons have you experienced with plastic diaphragm pumps?
10: The 4 primary plastics used in diaphragm pump wetted sections.
a) Polypropylene
For generic chemical transfer. It is the most common plastic used. About 35% of pump sales worldwide are polypropylene
b) PVDF (Kynar)
For use with highly concentrated oxidizers or strong oxidizers (such as bleach).
c) Conductive polypropylene
For use with general chemical transfer in a volatile or explosive atmosphere. It is electrically conductive from the black carbon in the plastic. These pumps are ATEX rated for worldwide use and NEMA rated for use in North America.
d) Acetal (Delrin)
Conductive plastic typically used for volatile solvents. Most plastics are not compatible with solvents and will swell. This quickly leads to pump failure and leakage. Acetal is solvent resistant and can pump flammable fluids.

Always count on Duplacao, your trusted supplier for pneumatic pumps. Get in touch by phone (48) 3438-8484 or email vendas@duplacao.com.br and talk to our experts.