Pressure in a fluid is defined as:
“the normal force per unit area exerted on an imaginary or real plane surface in a fluid or gas”
The pressure equation can be expressed as:
p = F / A (1)
Where
p = pressure (lb/in 2 (psi), lb/ft 2 (psf), N/m 2 , kg/ms 2 (Pa))
F = force (N) 1)
A = area (in 2 , foot 2 , m 2 )
1) In Imperial – English Engineering System, special care must be taken with the power unit. The base unit for mass is slug and the unit for force is pound ( lb ) or pound force ( lb f ).
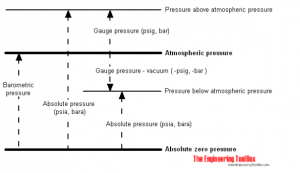
absolute pressure
A absolute pressure – p abs – is measured in relation to the pressure of the zero absolute – the pressure that would occur in an absolute vacuum. All calculations involving the gas law require that the pressure (and temperature) be in absolute units.
Manometric pressure
One measurer It is often used to measure the pressure difference between a system and the surrounding atmosphere. This pressure is often called gauge pressure and can be expressed as
p g = p s – p atm (2)
Where
p g = gauge pressure (Pa, psi)
p s = system pressure (Pa, psi)
p atm = atmospheric pressure (Pa, psi)
Atmospheric pressure
Atmospheric pressure is the pressure in the air surrounding – or “near” – the Earth's surface. Atmospheric pressure varies with temperature and altitude above sea level.
- Air density at altitude
standard atmospheric pressure
A Standard Atmospheric Pressure ( atm ) is commonly used as a reference when listing gas densities and volumes. Standard Atmospheric Pressure is set at sea level at 273 O K (0 O C) and is 1,01325 bar Where 101325 Pa (absolute) . the temperature of 293 O K (20 O C) is sometimes used.
In imperial units, standard atmospheric pressure is 14,696 psi.
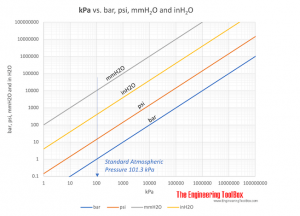
- 1 atm = 1,01325 bar = 101,3 kPa = 1,013 10 5 Pa = 14,696 psi (lb f /in 2 )= 760 mmHg = 10,33 mH 2 O = 760 torr = 29.92 inHg = 1013 mbar = 1.0332 kg f /cm 2 = 33,90 ftH 2O _
Pressure Units
As 1 Pa is a small unit of pressure, the hectoPascal (hPa) unit is widely used, especially in meteorology. The kiloPascal (kPa) unit is commonly used in the design of technical applications – such as HVAC systems, piping systems and the like.
- 1 hectoPascal = 100 Pascal = 1 milibar
- 1 kiloPascal = 1000 Pascal
Some pressure levels
- 10 Pa – pressure below 1 mm of water
- 1 kPa – approximately the pressure exerted by 10 g of mass in an area of 1 cm 2
- 10 kPa – the pressure below 1 m of water, or the drop in air pressure when rising from sea level to 1000 m altitude
- 10 MPa – nozzle pressure in a “high pressure” washer
- 10 GPa – enough pressure to form diamonds
Some Alternative Pressure Units
- 1 bar - 100,000 Pa
- 1 millibar - 100 Pa
- 1 atmosphere - 101325 Pa
- 1 mm Hg – 133 Pa
- 1 inch Hg – 3386 Pa
One torr (often used in vacuum applications) is named after Torricelli and is the pressure produced by a column of mercury of 1 mm de height – equal to 1/760 from an atmosphere.
- 1 atm = 760 torr = 14,696 psi = 1,013 bar
Pounds per square inch (psi) it was commonly used in the UK but is now replaced in almost every country except the US by SI units. As atmospheric pressure is of 14,696 psi – a column of air in an area of one square inch from Earth’s surface to space – weighs 14,696 pounds .
A barra (barra) is commonly used in industry. a bar is 100.000 Pa and, for practical purposes, can be approximated to an atmosphere even if
1 bar = 0,9869 atm = 14,5 psi
They exist 1000 milibares (mbar) in a bar , a common unit in meteorology and meteorological applications.
1 milibar = 0,001 bar = 0,750 torr = 100 Pa
Source: https://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/pressure-d_587.html










