The affinity laws of turbo machines can be used to calculate the volume capacity, head or energy consumption in centrifugal pumps when changing speed or wheel diameters.
As Leis Affinity values of centrifugal pumps or fans indicate the influence on the volume capacity, head (pressure) and/or energy consumption of a pump or fan due to
- change in velocity wheel speed – revolutions per minute (rpm)
- geometric similarity – change in impeller diameter
Note that there are two sets of affinity laws:
- affinity laws for a specific centrifugal pump – to approximate height, capacity and power curves for different motor speeds and/or different impeller diameters
- affinity laws for a family of geometrically similar centrifugal pumps – to approximate load, capacity and power curves for different motor speeds and/or different impeller diameters
Pump affinity laws for a specific centrifugal pump
Volume Capacity
The volumetric capacity of a centrifugal pump can be expressed as
q 1 / q 2 = (n 1 / n 2 ) (d 1 / d 2 ) (1)
Where
q = volume flow capacity (m 3 /s, gpm, cfm, ..)
n = wheel speed – rotation per minute – (rpm)
d = diameter of the stem (m, pés)
Head or Pressure
The head or pressure of a centrifugal pump can be expressed as
dp 1 / dp 2 = (n 1 / n 2 ) 2 (d 1 / d 2 ) 2 (2)
Where
dp = load or pressure (m, ft, Pa, psi, ..)
Can
The energy consumption of a centrifugal pump can be expressed as
P 1 / P 2 = (n 1 / n 2 ) 3 (d 1 / d 2 ) 3 (3)
Where
P = power (W, bhp, ..)
Changing the Wheel Speed
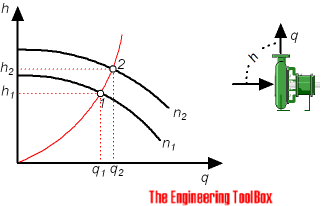
Se o wheel diameter is constant – changing pump wheel speed can simplify affinity laws to
Volume Capacity
q 1 / q 2 = (n 1 / n 2 ) (1a)
Head or Pressure
dp 1 / dp 2 = (n 1 / n 2 ) 2 (2a)
Can
P 1 / P 2 = (n 1 / n 2 ) 3 (3a)
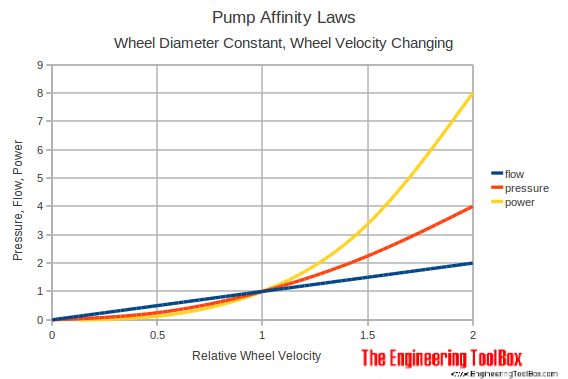
Observation! If the speed of a pump is increased by 10%
- volume flow increases with 10%
- the head grows with 21%
- the power increases with 33%
If we want to increase the flow capacity of an existing system in 10% , we have to increase the power supply by 33% .
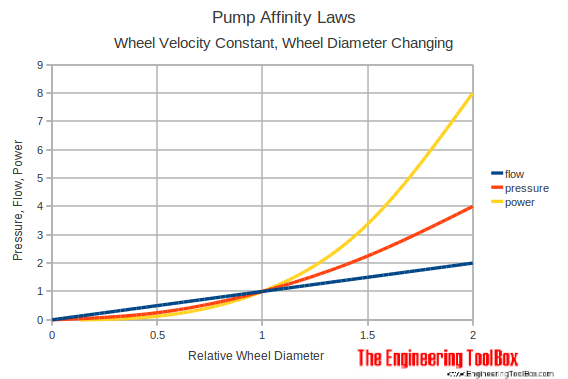
Changing the Impeller Diameter
If the speed of the wheel is constant, a change in rotor diameter simplifies the affinity laws to
Volume Capacity
q 1 / q 2 = d 1 / d 2 (1b)
Head or Pressure
dp 1 / dp 2 = (d 1 / d 2 ) 2 (2b)
Can
P 1 / P 2 = (d 1 / d 2 ) 3 (3b)
Example – Pump Affinity Laws – Changing Pump Speed
Pump speed is changed when impeller size is constant. The initial flow is 100 gpm , the initial head is from 100 feet , the initial power is the 5 bhp , the initial speed is 1750 rpm and the final speed of 3500 rpm .
The final flow capacity can be calculated with (1a):
q 2 = q 1 n 2 / n 1
= (100 gpm) (3500 rpm) / (1750 rpm)
= 200 gpm
The final head can be calculated with (2a):
dp 2 = dp 1 (n 2 / n 1 ) 2
= (100 pes) ((3500 rpm) / (1750 rpm)) 2
= 400 feet
The final energy consumption can be calculated with (3a):
P 2 = P 1 (n 2 / n 1 ) 3
= (5 cv) ((3500 rpm) / (1750 rpm)) 3
= 40 cv
Example – Pump Affinity Laws – Changing Impeller Diameter
Pump impeller diameter is reduced when pump speed is constant. The diameter is changed from 8 to 6 inches .
The final flow capacity can be calculated with (1b) :
q 2 = q 1 (d 2 / d 1 )
= (100 gpm) ((¨6 in) / (8 in))
= 75 gpm
The final head can be calculated with (2b) :
dp 2 = dp 1 (d 2 / d 1 ) 2
= (100 pes) ((6 pol) / (8 pol)) 2
= 56.3 feet
The final energy consumption can be calculated with (3b) :
P 2 = P 1 (d 2 / d 1 ) 3
= (5 cv) ((6 half) / (8 half)) 3
= 2,1 cv
Pump affinity laws for a family of geometrically similar pumps
The volume capacity can be expressed as
q 1 / q 2 = (n 1 / n 2 )(d 1 / d 2 ) 3 (4)
Where
q = volume flow capacity (m 3 /s, gpm, cfm, ..)
n = wheel speed – rotation per minute – (rpm)
d = wheel diameter
Head or Pressure
The head or pressure of a centrifugal pump can be expressed as
dp 1 / dp 2 = (n 1 / n 2 ) 2 (d 1 / d 2 ) 2 (5)
Where
dp = load or pressure (m, ft, Pa, psi, ..)
Can
The energy consumption of a centrifugal pump can be expressed as
P 1 / P 2 = (n 1 / n 2 ) 3 (d 1 / d 2 ) 5 (6)
Where
P = power (W, bhp, ..)
Note that the affinity laws for fans are not the same as for pumps.
Source: https://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/affinity-laws-d_408.html